
| Home | Overview | Manual | Contact |
| Version 2.0 |
The BindUP-Alpha website provides information on the electrostatic patches on protein surfaces and predicts NA-binding propensity given a 3D structure or a structural model of a protein (1).
The algorithm incorporates two independent structure-based machine learning methods. Both methods calculate structural and electrostatic features of the protein based on its 3D representation. For calculating the surface features, we first extract the positive and negative surface patches using the PatchFinder algorithm, originally developed for annotating DNA- and RNA-binding proteins (2, 3).
For experimentally solved protein structures, physiochemical features and surface patches are calculated per individual protein chain (4, 5).
For predicted protein structures, when only a protein sequence and a structural model are available, the physiochemical features and the surface patches are calculated from the largest well-defined domain, obtained from the 3D structural model. In addition to the structure-based features, we calculate diverse properties derived from the protein sequence - intrinsic disorder propensities (IDR) and other biochemical features (1).
The calculated features are combined into a feature vector, which is then fed into a Support Vector Machine (SVM) to predict whether the protein is an NABP.
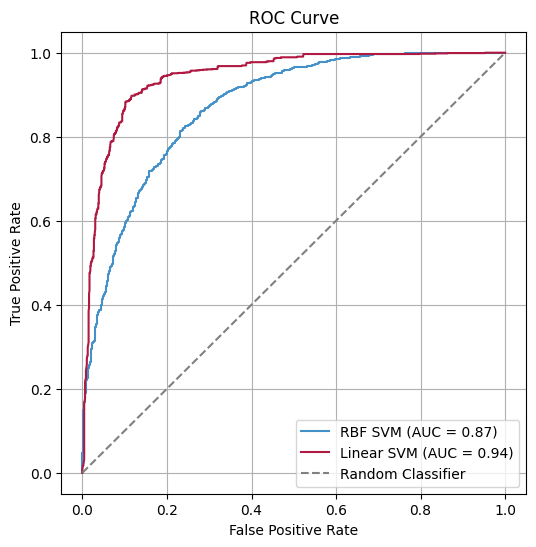
BindUP-Alpha achieves high accuracy in predicting DNA- and RNA-binding proteins.
- Alexandrovich D, Kagan S, Mandel-Gutfreund Y. BindUP-Alpha: A Webserver for Predicting DNA- and RNA-Binding Proteins based on Experimental and Computational Structural Models, 2025. (Under Revision)
- Stawiski EW, Gregoret LM, Mandel-Gutfreund Y. Annotating nucleic acid-binding function based on protein structure. J Mol Biol. 2003;326(4):1065-1079.
- Shazman S, Celniker G, Haber O, Glaser F, Mandel-Gutfreund Y. Patch Finder Plus (PFplus): a web server for extracting and displaying positive electrostatic patches on protein surfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(Web Server issue):W526-W530.
- Shazman S, Mandel-Gutfreund Y. Classifying RNA-binding proteins based on electrostatic properties. PLoS Comput Biol. 2008;4(8):e1000146. Published 2008 Aug 8.
- Paz I, Kligun E, Bengad B, Mandel-Gutfreund Y. BindUP: a web server for non-homology-based prediction of DNA and RNA binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(W1):W568-W574.